Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS – Lou Gehrig’s disease)

Tid Bits of Info
- Amyotrophic: A “no”, myo “muscle”, trophic “nourishment”: “no muscle nourishment” which leads to atrophy and wasting away.
- Less than 10% or the cases of ALS are due to heredity.
- ALS can be very variable and not everyone suffers the severe symptoms.
- Smoking and lead exposure are possible links to the disease.
- Physical therapy can help a person maintain independence prolong their life.
Why are so many people dumping buckets of ice water on their heads in the United States? They’re raising funds and bringing attention to the devastating disease Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS). The most common motor neuron disease, ALS is a progressive neurologic disease that causes severe loss of muscle action and function. The disease has no cure and can cause death within a few years of the original diagnosis.
Most people know ALS by the common term “Lou Gehrig’s disease.” Gehrig was a great professional baseball player for the New York Yankees until the disease forced him to retire in the late 1930’s. While research has helped improve understanding of the disease, treatment is still limited and there is no known cure. Increased funding could go a long way toward addressing this situation.
The “ice bucket challenge” has directly addressed this lack of awareness and lack of funding. In the challenge, you make a video of dumping a bucket of ice water on your head. During the video, participants talk about the disease and the need for a cure, pledge to make a donation, and then challenge friends to do the same. This challenge is helping the world learn about the disease and the need for a cure.
Effects of ALS
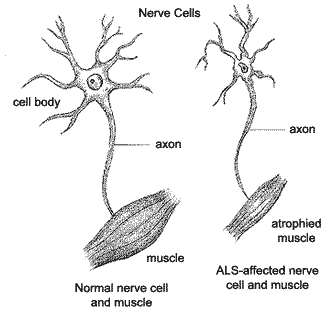
Many Americans are now trying to learn more about Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis. ALS is progressive and effects the nerve cells within the brain and spinal cord that are responsible for motor control or movement. There are different types of nerves within the human body and some are responsible for transmitting a signal from the brain and spinal cord to a particular muscle.
These “motor neurons” are the nerve cells that are degenerative in the person with ALS. These cells eventually die and the brain and spinal cord are incapable of transmitting a signal to the particular muscle. Once this occurs the person will eventually be unable to move voluntarily and becomes paralyzed. The anterior horn of the spinal cord houses the motor neurons. The posterior horn receives sensory information. When the motor neurons die, the anterior, lateral aspect of the spinal cord begins to harden (sclerosis) with scar.
The motor neurons control voluntary movements. The ability to move, speak, eat and breathe are effected therefore the disease usually is fatal. There is no known cause and the treatments that are used at this time are designed to slow down the progression of the disease.
Symptoms of ALS
There are some early signs of the disease. If you or someone you knows has presented with these signs and symptoms seek medical advice and treatment.
- Difficulty walking and losing balance
- Weakness in your limbs
- Difficulty grasping and handling materials
- Muscle cramps and twitches
- Difficulty speaking and slurring speech
- Difficulty maintaining good posture and holding your head up.
Fortunately and unfortunately this disease rarely affects involuntary muscle action. The heart continues to beat, the GI tract continues to function and there is no loss of mental capacity in most cases. This enables people with this disease to remain “active” in their family, work and other aspects of their lives.
There is no known cause at this time. Research revolves around heredity and gene mutation, chemical imbalances within the body, abnormalities in the immune system and the inability of the cells to utilize certain proteins correctly. The disease usually strikes people between the ages of 30 – 65 and men are more affected than women.
The actual diagnosis is difficult. The doctor will most likely order EMG (electromyogram), nerve conduction studies, MRI, blood and urine tests, spinal tap (lumbar puncture) and possibly a muscle biopsy. The difficulty with a definitive diagnosis lies in the fact that there are many neurological disorders and diseases that present with similar signs and symptoms.
The treatment is geared at slowing down the progression of the disease. Many people die within 3-5 years of the initial diagnosis. Physical therapy and occupational therapy are used to help the patient learn how to adapt and modify their lifestyle and activities as their bodies change. Exercise is recommended to help strengthen any muscle or groups of muscles that have not been affected by the disease. Unfortunately, the disease eventually affects all muscles of the body.
ALS is a progressive neurodegenerative disease that has no known cause or cure. The disease is fatal in most instances and the treatment is designed to slow down the progression and help the patient maintain what functional capabilities that they are capable of performing as their body weakens.