BENNETT FRACTURE

Tid Bits of Info
- 80% of all thumb fractures involve the base of the metacarpal bone.
- Bennett fractures involve the articular surface and can pre-dispose the joint to arthritic changes in the future.
- Bennett fractures occur when an excessive load is placed on a partially flexed thumb joint.
- Surgery usually reduces the length of the rehabilitation time because motion can begin more quickly.
- Seek the advice and treatment of a Physical Therapist if you have suffered a Bennett fracture an need to rehabilitate your thumb.
Whether hiking in the mountains, playing sports, or simply walking through the house, we may accidentally fall. For most of us, the natural tendency is to break the fall with outstretched arms. Unfortunately, our hands or arms receive the force of impact. This force is great enough to injure the bones in the hands or wrist. The impact force can even cause an outstretched thumb to fracture at the base. This type of fracture is the most commonly occurring fracture to the base of the first metacarpal and known as a Bennett fracture. With proper medical treatment and rehabilitation, the thumb should regain full mobility.
The wrist/hand complex is made up from carpal bones, metacarpal bones and phalanges which are located in each finger. The metacarpal bones are located in the “palm” of the hand and the proximal end (closest to the wrist) of each metacarpal is referred to as the base of the metacarpal. The opposite end is the head and the “shaft “connects the base and head. The Bennett fracture occurs when the axial load on the thumb side metacarpal (1st metacarpal) is too great and the bone fails at the base. The fracture site includes part of the articulating aspect of the carpal metacarpal joint or CMC. Depending on the severity of the fracture and the quality of fixation this injury can pre-dispose someone’s thumb to suffer from arthritis in the future.
Accurate diagnosis via X-rays is required to establish the proper plan of care. There are 3 classifications of Bennett fractures. Type 1 has a single ulnar fragment. Type 2 is an impact fracture without subluxation of the first metacarpal and finally Type 3 is a combination of an ulnar fragment and metacarpal dislocation. The severity and type of fracture determine how the patient’s injured thumb is treated by the orthopaedic doctor.
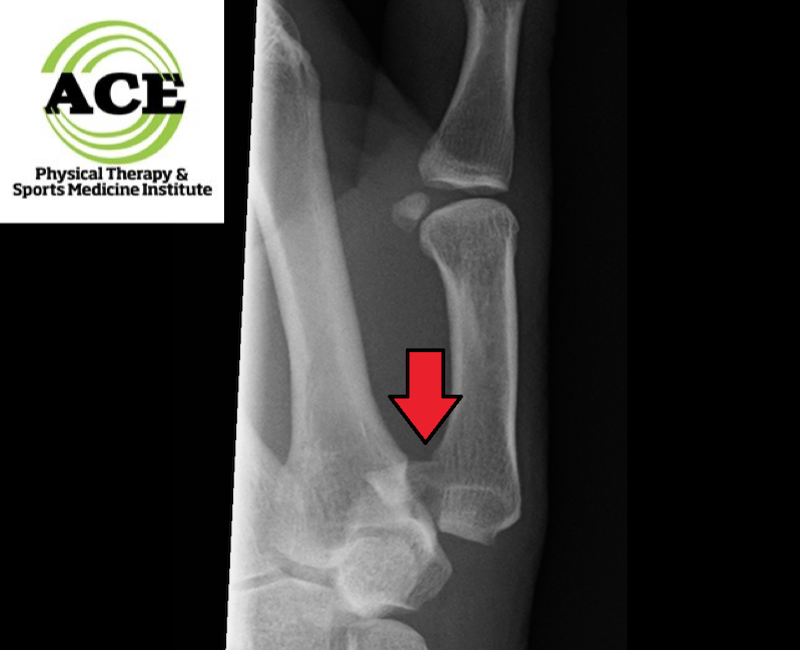
In the past and with a simple single fragment, the choice is usually to put the injured thumb in a cast and allow it to heal. When the injury is determined to more severe, the thumb might be reduced and fixated via a surgical procedure. Open reduction and internal fixation (ORIF) surgery is common and highly successful. The surgeon will fixate the injury to within 1mm of the original bony anatomy because it has been determined that this is needed to enable full return of function and not pre-dispose the injured joint to future arthritic changes and pain.
Following a period of immobility, Physical or Occupational Therapy is started to restore motion in the wrist, fingers and thumb. The period of immobility is longer if surgery is not performed therefore many doctors choose to perform a surgery to reduce the time of immobility. When the thumb is immobilized for a long period of time (6-8 weeks) the bone heals well, but there can be detrimental changes to the muscles, joint capsules and articular cartilage. The entire limb can be negatively affected.
In the past and in certain settings, Occupational Therapists were the providers of rehabilitation services for any upper extremity injury. Today, many and most out-patient Physical Therapists can develop and implement a treatment protocols that are geared at restoring full function and use of the injured hand. This protocol would include exercises that involve the entire arm and core. If the immobility period is extensive, there will be more “collateral” involvement of the entire involved limb.
Bennett fractures usually occur when the thumb is partially flexed and there is large axial load applied to the thumb (i.e. falling on an out-stretched hand). These fractures are reduced and immobilized and the severity of the fracture determines how the fracture site is treated. The length of immobility is one of the primary factors that determine how long the complete rehabilitation process will last. Bennett fractures are the most commonly occurring fracture to the base of the thumb and with proper treatment protocols the thumb will regain full functional capability.
























